Source: Wikipedia
The two ways of international arms transfer are:
➠Arms Trade
➠Arms Aid
Because of the secret nature of many arms transaction, the difficulty arises in describing the boundaries of each of the above 2 categories.
Arms Trade in simpler terms is the process via which manufacturing countries along with private companies sell their weapons systems in the international arms market. Just like any other market fierce competition exist among the arms-producing nations/companies exist in the non-producing countries.
Arms trade also exist among the producing nations/companies as one of them might not have the expertise or have an inadequate domestic production.Therefore arms trade can be classified into 3 categories:
Arms trade also exist among the producing nations/companies as one of them might not have the expertise or have an inadequate domestic production.Therefore arms trade can be classified into 3 categories:
➠Between the allied or friend~ developed countries;
➠Between the developed and the developing countries; and,
➠Amongst the developing countries.
These categories reflect:
〼Sale of arms - It is the licensed sale of any weapon system which may or may be associated with any condition. The end user restriction is often used to prevent and deter the sales and diversion of arms supplies. In some cases, import certificates are required to make necessary payments
〼Weapons and arms supply to any bloc or alliance members.
〼Resale of surplus or old weapons (In the US under 1033 program excess military equipment were transferred to civilian law enforcement agencies.(1))
〼Premptive selling - It is done to maintain an equilibrium within a given region (from suppliers point of view) and to prevent the development of an advantageous position of their rival power.
〼In many instances, governments sanction the transfer of surplus weapons through private channels.
〼Another mode of acquisition of arms is through contraband and stolen arms shipments. This method is mostly used by insurgent forces to acquire weapons, or for copying and studying the weapons systems used by the members of the opposing blocs.
〼Many weapons are captured during wars and then sold to interested parties, such as the sale of the Soviet weapons to the USA, and so on.
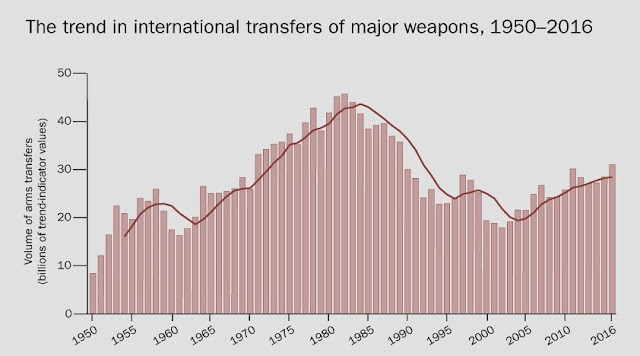 |
| Source: SIPRI (Stockholm International Peace Research Institute) |
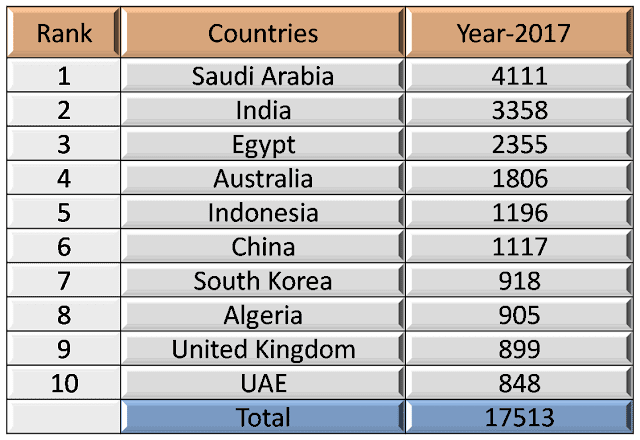 |
| Top 10 Countries Importing Arms(2) |
Key Facts(3)
Global spending on arms
- The world spent $1.69 trillion on the military in 2016, just over 2% of global GDP.
- The top 100 arms companies have sold over 5 trillion dollars’ worth of arms since 2002.
Global exports and imports of major conventional weapons
- In the last five years, transfers of major conventional weapons reached their highest volume since the end of the Cold War.
- China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom and the United States, the five permanent members of the UN Security Council, a body charged with the maintenance of international peace and security – are collectively responsible for over 70% of the arms trade.
- The US and Russia are responsible for over half of all weapons exports globally.
Transfers to the Middle East
- Over a quarter of global exports of major conventional weapons go to countries in the Middle East and North Africa region.
- The US, the UK, and France are responsible for around 70% of all exports of major conventional weapons to the Middle East.
- In the last five years, the Gulf states have massively increased their imports of major conventional weapons - Saudi Arabia has imported 212 % more than over the previous five years), with the United Arab Emirates up 63%, Qatar up 245% and Kuwait up 175%.
Saudi Arabia-Yemen
- In May 2017, the US announced $110 billion worth of potential arms sales to Saudi Arabia – consolidating past and present negotiations.
- The potential sales include $4.6 billion worth of guided air-to-ground munitions - a total of 104,000 bombs of the type that have been used routinely in the Yemen War.
- The UK has approved exports of licenses worth over £3.7 billion to Saudi Arabia since the beginning of the most recent conflict in Yemen.
Small Arms and Light Weapons
- Eight million new small arms and up to 15 billion rounds of ammunition are manufactured each year.
- The small arms trade is worth an estimated US$8.5 billion per year.
- Two billion dollars’ worth of small arms ammunition transfers were reported to UN Comtrade in 2013; one billion dollars’ worth of pistols and revolvers were reported for the same period.
Conflict
- 2,238,326 people have died in armed conflicts since the end of the Cold War – with over 100,000 in 2016 (4).
- The aggregate economic and financial cost of violence in 2016 was estimated to be $14.3 trillion, or 12.6% of the global economy.
Trade Trend 2017
- The volume of international transfers of major weapons has grown steadily since 2003. In 2013–17 the volume was 10 percent higher than in 2008–12.
- The five largest exporters in 2013–17 were the USA, Russia, France, Germany, and China. Together, they accounted for 74 percent of the total volume of arms exports.
- US exports accounted for 34 percent of the global total in 2013–17. US arms exports in 2013–17 grew by 25 percent compared with 2008–12.
- French and Chinese arms exports in 2013–17 were higher than in 2008-12, with respective increases of 27 and 38 percent.
- Russian arms exports decreased by 7.1 percent between 2008–12 and 2013–17, and German exports fell by 14 percent.
- The five largest importers in 2013–17 were India, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, the UAE, and China. Together, they received 35 percent of all arms imports.
- The main recipient region in 2013–17 was
⇒Middle East (32 percent),
⇒Europe (11 percent),
⇒Africa (7.2 percent)
⇒Americas (7.1 percent).
- Between 2008 12 and 2013–17arms imports by states in the Middle East and Asia and Oceania increased by 103 and 1.8 percent, respectively.
- By contrast, overall imports decreased in the
⇒Africa (–22 percent)
⇒Europe (–22 percent)


.jpg)

No comments:
Post a Comment